Boost Your Business Up
Ranking High Level
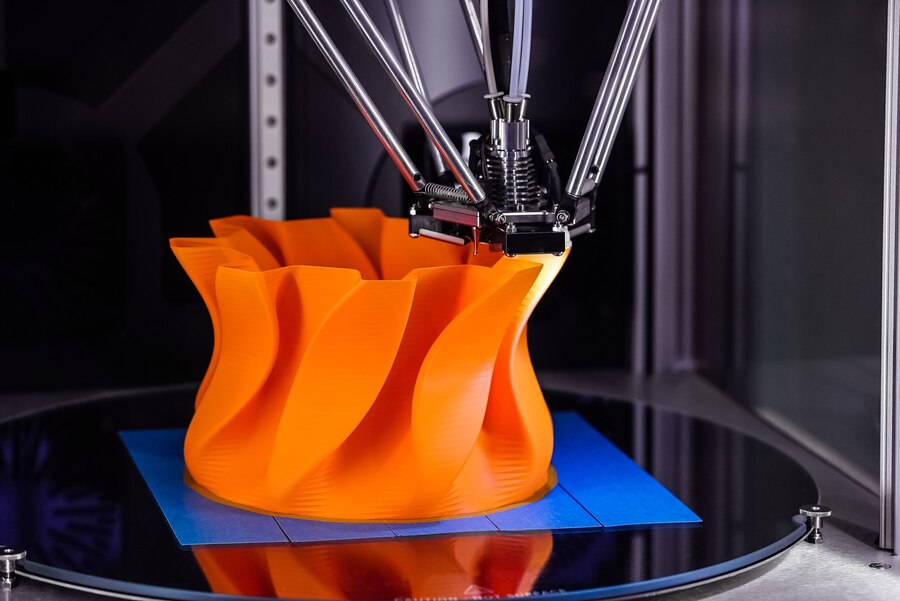
FDM
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) 3D printers build objects by extruding heated thermoplastic filaments layer by layer. Known for affordability, versatility, and ease of use, they're ideal for prototyping, hobby projects, and small-scale production. Popular filaments like PLA, ABS, and PETG offer durability, flexibility, and precision. Industries such as automotive, healthcare, and education widely use FDM printers for rapid prototyping, functional testing, and custom part manufacturing. Their accessibility makes them perfect for beginners and professionals, supporting innovation across diverse fields.
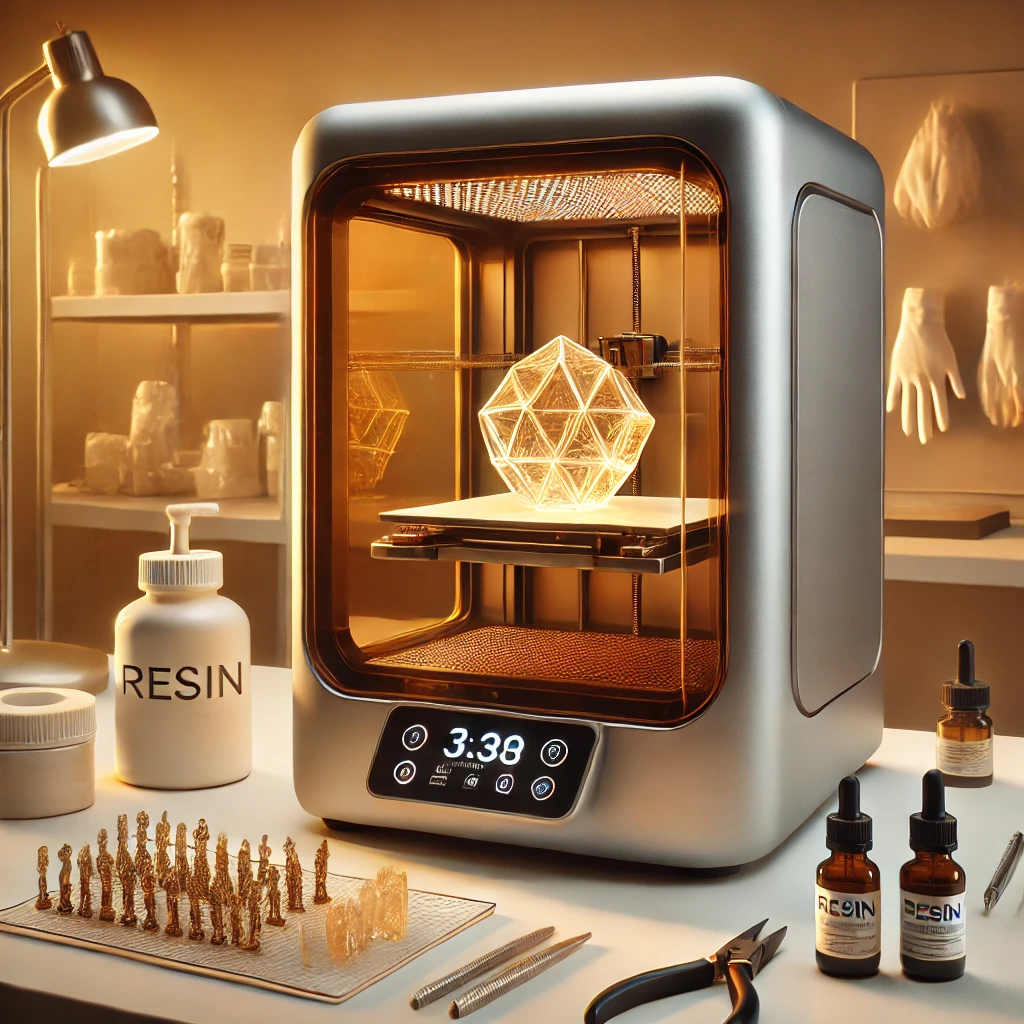
Resin 3D Printers
Resin 3D printers use SLA (Stereolithography) or DLP (Digital Light Processing) technology to create high-precision objects by curing liquid resin with UV light. Known for their exceptional detail, smooth surfaces, and accuracy, they excel in applications requiring fine resolution, such as jewelry design, dental models, and miniature figurines. Common resins include standard, flexible, and tough variants, each tailored for specific needs. While they offer unmatched detail, resin printers require post-processing, including washing and curing. Industries like healthcare, prototyping, and art benefit from resin 3D printing for creating intricate, durable, and visually appealing products.
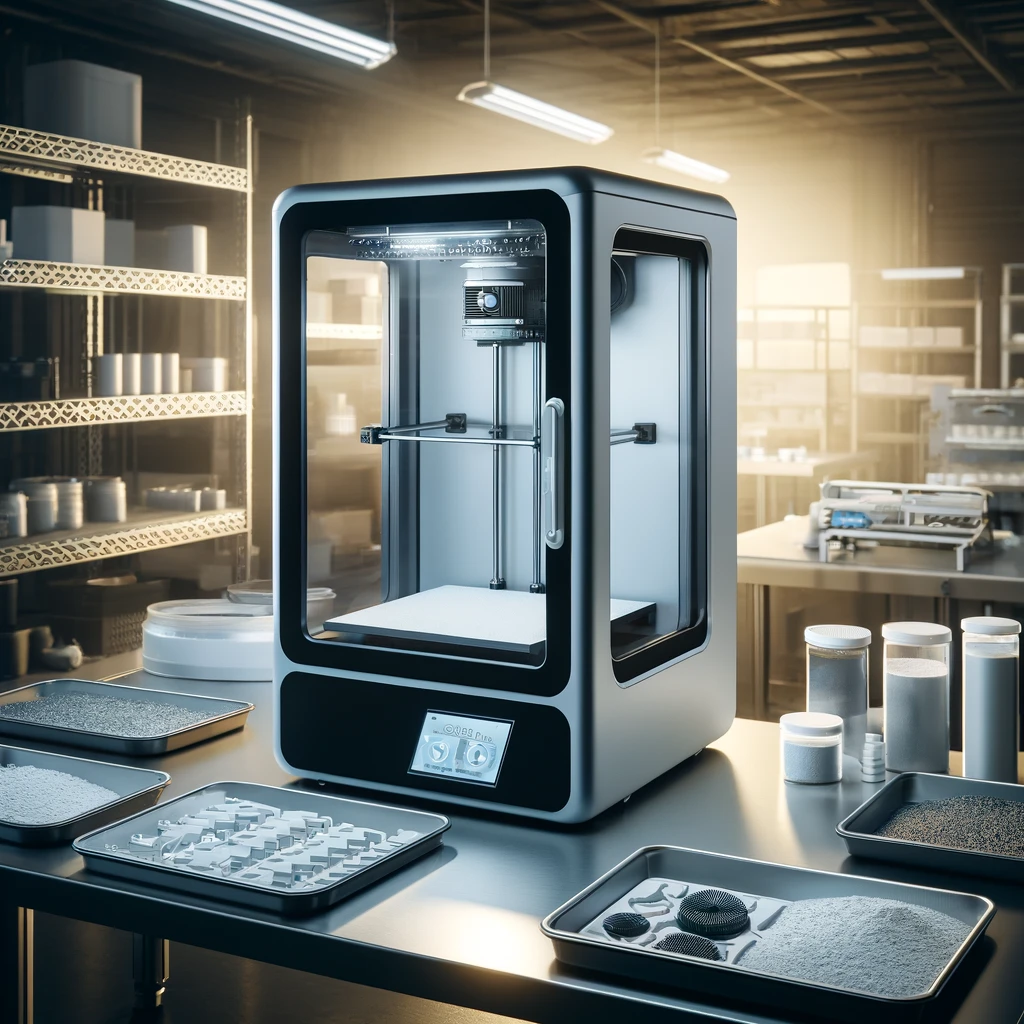


SLS 3D Printers
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D printers use a high-powered laser to fuse powdered materials, typically nylon or other polymers, layer by layer to create durable and complex parts. Known for their precision and strength, SLS printers are ideal for functional prototypes and end-use parts without requiring support structures. They excel in industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical, offering design flexibility and high-quality finishes for intricate geometries. SLS technology enables rapid production of lightweight components, reducing material waste and manufacturing time. Its ability to produce consistent, repeatable results makes it a preferred choice for both low-volume production and customized solutions.
3D Scanners
3D scanners capture the shape and dimensions of objects by analyzing their surface and geometry, creating precise digital 3D models. Using technologies like laser scanning, structured light, or photogrammetry, they are essential for reverse engineering, quality control, and digital preservation. Industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and entertainment rely on 3D scanners for tasks like creating custom prosthetics, replicating artifacts, or generating CGI assets, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in design workflows.

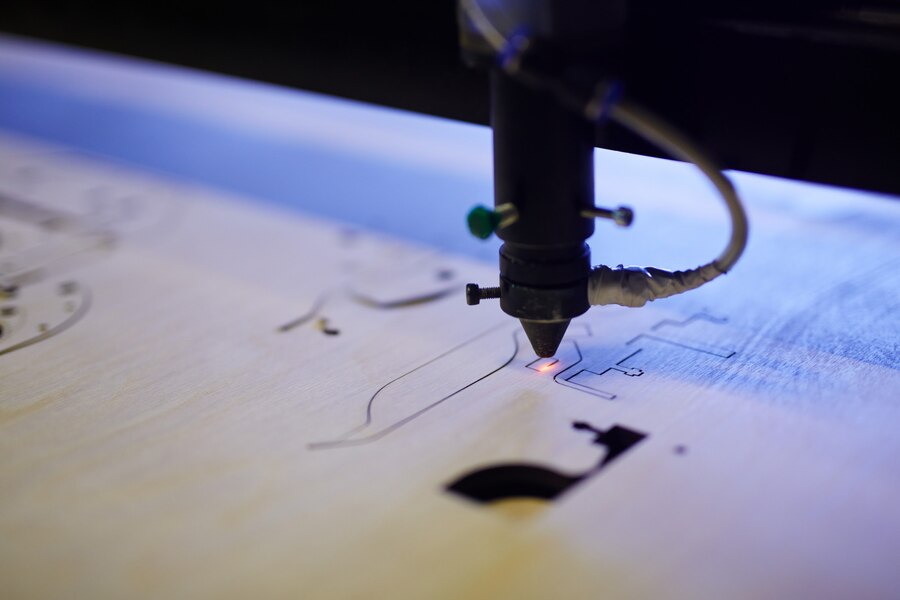
Laser engravers
Laser engravers use focused laser beams to etch designs, patterns, or text onto various materials, including wood, metal, glass, and plastic. Known for their precision and versatility, they are widely used in industries like manufacturing, jewelry, and customization. From intricate artwork to industrial barcodes, laser engravers offer high accuracy and speed, enabling both creative and functional applications. They are essential tools for personalized products and detailed craftsmanship.
